As the name suggests, gas is used as energy in gas turbines, and the energy obtained from gas is much cheaper than the energy obtained from water vapor used in steam turbines. Also, in a gas turbine, when there is no gas for some reason, diesel liquid fuel can be used. These two factors are among the most important advantages and privileges of gas turbines. Because these turbines are rotated by the force of gas expansion, they are called Turbo Expander
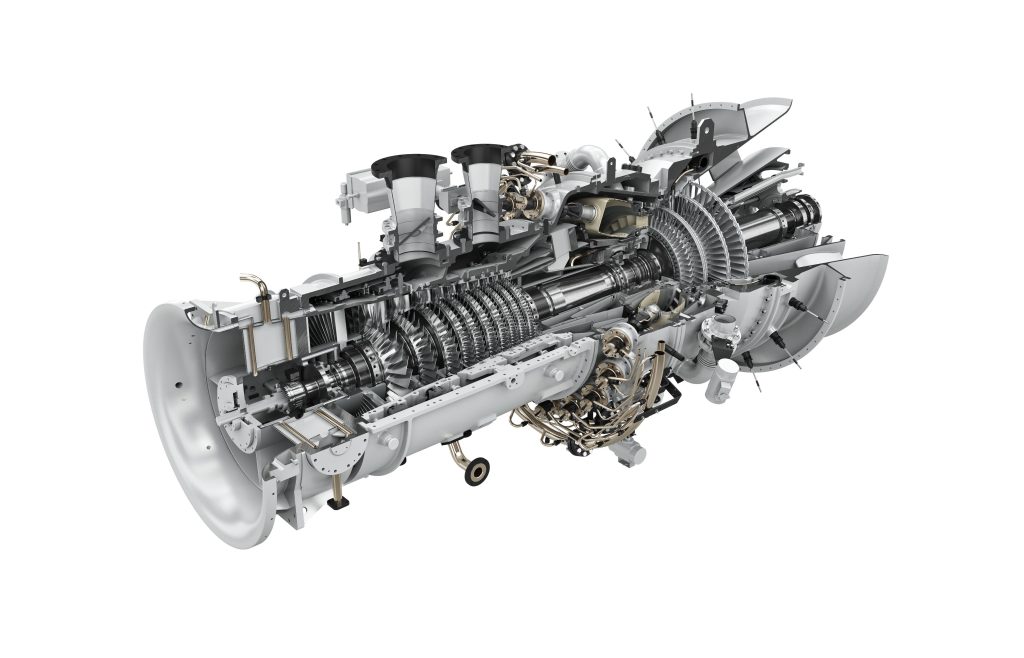
To use the energy in gas or diesel, they must be burned in the vicinity of air. Therefore, the gas turbine must have a combustion chamber and an air compressor. In general, a gas turbine consists of three main parts: compressor, combustion chamber, and turbine. Also, the air intake and exhaust equipment include the first part and the last part of a gas turbine, respectively
The basis of work in a gas turbine is that in the first stage, a large volume of air is sucked into the compressor after being purified by filters with atmospheric pressure and ambient temperature through the inlet called Engine Air Inlet. It faces an increase in temperature, an increase in pressure, and a decrease in volume, and finally, the air comes out of the compressor with high pressure and temperature
In the second step, the compressed air enters the combustion chamber through the airflow channel. In this section, by injecting fuel, combustion takes place at constant pressure and a flame is formed. In the process of combustion, the gases undergo volume expansion and finally the hot compressed expanded gases with high pressure and temperature leave the combustion chamber
In the third stage, the working fluid enters the turbine section and by overcoming the resistive force and doing the work, it sets the turbine blades in motion and causes the rotational power of the shaft, and creates thrust reaction force or a combination of both. In the turbine part, the fluid faces a pressure drop while passing through the blades and expands until it reaches the ambient pressure. Finally, the fluid with atmospheric pressure and high temperature leaves the turbine and enters the free environment through the exhaust
The compressor used in gas turbines is mostly of the centrifugal or axial flow type, which consists of several rows of fixed blades and rotating blades. In order to compress the air from one stage to the next, the vanes are placed in such a way that they get smaller from the inlet to the outlet
In the turbine part, the necessary energy to overcome the friction force, and turn the turbine and other equipment that are mounted on the turbine axis must be provided, which is the same for all types of water, steam, gas, and wind turbines
A lot of energy is needed to perform the above steps, so to produce more energy, the volume of air that enters the combustion chamber must be much more than the air needed to burn gas or diesel. When the combustion occurs, the excess of the incoming air is also heated and its volume increases and its pressure rises. Therefore, the building of the combustion chamber is built in such a way that the air coming out of the compressor cannot extinguish the flame in the combustion chamber due to its pressure
In the turbine, the position of the fixed and rotating blades is the opposite of the compressor, and they get bigger from the inlet to the outlet respectively. This increase in the length of the turbine blades is for pressure drop and speed increase, and this means the conversion of pressure energy into kinetic energy. The compressor part and the turbine part can consist of a consecutive number of stages (each stage is a disk on which the blades are installed)